- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
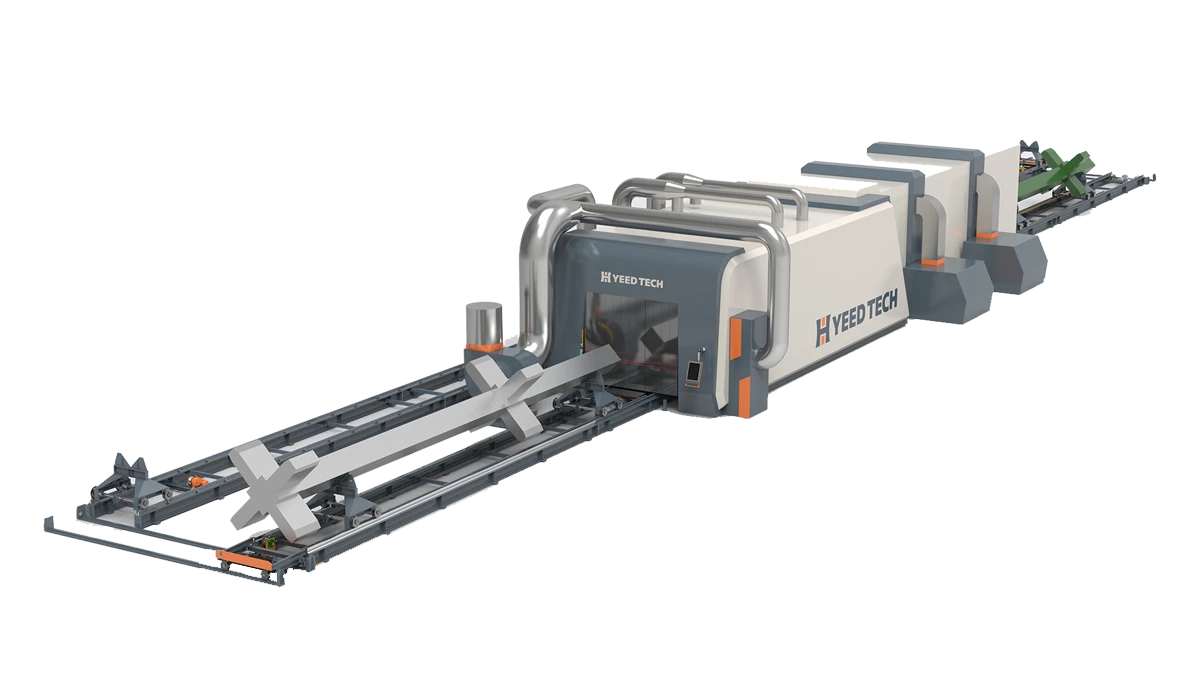
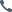
Spray Painting Line Safety Protocols
Implementing comprehensive safety measures is crucial when operating spray painting line systems for steel structure painting applications. This guide outlines essential safety protocols for automatic painting line operations, ensuring worker protection and process efficiency in industrial coating environments.

Personal Protective Equipment for Spray Painting Line
• NIOSH-approved respirators with organic vapor filters for spray painting line operators
• Full-body protective suits resistant to paint solvents
• Safety goggles with anti-fog coating for clear visibility
• Chemical-resistant gloves with textured grip
• Steel-toe boots with anti-slip soles for steel structure painting areas
• Hearing protection in high-noise automatic painting line environments
• Emergency eyewash stations within 10 seconds access
• Proper ventilation masks for confined space operations
Equipment Safety in Automatic Painting Line
• Emergency stop buttons every 6 meters along spray painting line
• Grounding systems to prevent static electricity buildup
• Interlocked safety gates on automatic painting line enclosures
• Regular calibration of spray gun pressure regulators
• Automated fire suppression systems in paint booths
• Scissor lift mechanisms with 3.5T capacity for steel structure painting
• Chain collision avoidance sensors in material handling
• Overload protection on conveyor systems
Ventilation and Fume Control for Steel Structure Painting
• Minimum 100 fpm airflow in spray painting line booths
• Two-stage filtration (pre-filter + HEPA) in exhaust systems
• Real-time VOC monitoring with alarm triggers
• Explosion-proof exhaust fans for automatic painting line
• Proper ductwork maintenance schedules
• Negative pressure maintenance in paint mixing areas
• Fresh air supply calculations per operator
• Regular air quality testing protocols
Chemical Handling in Spray Painting Line
• Proper labeling of all paint containers in steel structure painting areas
• Secondary containment for bulk storage
• Compatible material construction for automatic painting line fluid systems
• Spill response kits every 15 meters
• Flashpoint monitoring for paint products
• Bonding and grounding during transfer operations
• Maximum allowable quantities per fire code
• SDS accessibility within 30 seconds
Training Requirements
• Initial 40-hour certification for spray painting line operators
• Quarterly refresher courses on steel structure painting safety
• Lockout/tagout procedures for maintenance
• Emergency response drills every 6 months
• Equipment-specific training for automatic painting line models
• Hazard communication program updates
• First aid/CPR certification for supervisors
• Confined space entry training where applicable
Spray Painting Line FAQs
Q: What safety measures are essential for a spray painting line?
A: A spray painting line requires strict safety measures to protect workers and prevent hazards. These include proper ventilation systems to remove toxic fumes and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), along with gas detectors to monitor air quality. Emergency stop buttons at key points allow instant shutdowns, while fire suppression systems (like sprinklers or dry chemical extinguishers) mitigate fire risks from flammable paints. Safety barriers and interlocks restrict access to moving parts, and operators must wear PPE such as respirators, goggles, and chemical-resistant gloves. Regular equipment inspections and staff training on handling spills or leaks are also critical.
Q: How to ensure uniform coverage in steel structure painting?
A: Ensuring uniform coverage in steel structure painting starts with surface preparation—cleaning rust, dirt, and old paint, then applying a primer to create a smooth base. Using high-pressure spray systems with calibrated nozzles helps distribute paint evenly, especially on large or irregular surfaces. Maintaining consistent spray distance (typically 8–12 inches) and overlapping each pass by 50% prevents thin spots. For vertical structures, work from top to bottom to avoid drips. Adjusting paint viscosity (with thinners if needed) and ensuring the line’s conveyor speed matches drying times also reduces unevenness. Testing on sample pieces first allows for setting tweaks before full-scale application.
Q: What maintenance does an automatic painting line require?
A: An automatic painting line needs regular maintenance to sustain performance. Daily tasks include cleaning spray nozzles and hoses to prevent clogs, checking for paint leaks, and emptying overspray collection systems. Weekly, lubricate moving parts (conveyor belts, pumps) and inspect filters, replacing them if clogged to protect pumps. Monthly, calibrate pressure settings and check sensors for accuracy—dust or paint buildup can disrupt readings. Quarterly, deep-clean reservoirs and inspect seals/gaskets for wear, replacing them to avoid leaks. For software-driven lines, update programs periodically and test emergency stop functions to ensure reliability. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule extends equipment life and reduces downtime.
Q: Can a spray painting line handle different types of paint for varied materials?
A: Yes, a spray painting line can handle different paints for varied materials with adjustments. For metal, use epoxy or polyurethane paints and adjust pressure for better adhesion. Wood may require low-pressure settings and water-based paints to prevent warping. Plastics often need specialized primers and electrostatic spray systems to improve paint grip. Line modifications like heated drying zones work for heat-cured paints (e.g., for ceramics), while changing nozzles (wider for large surfaces, finer for details) and adjusting paint flow rates accommodate viscosity differences between thick primers and thin topcoats. Most lines allow quick switching of paint reservoirs and cleaning protocols to avoid cross-contamination.
Q: What factors affect the cost of setting up an automatic painting line?
A: The cost of setting up an automatic painting line depends on several factors. Line size is key—small lines for parts (e.g., hardware) cost less than industrial-scale systems for large structures. Automation level matters: basic lines with fixed sprayers are cheaper than fully robotic systems with AI-driven adjustments. Additional features like climate control (for consistent drying), overspray recovery systems, or multi-color capabilities add expense. Material compatibility (e.g., explosion-proof components for flammable paints) increases costs, as do customizations for unique part shapes. Installation charges (including electrical/water connections) and training for operators also contribute, with total costs ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars for high-end industrial lines.
Products Categories
Latest News
-
Unveiling the World of Container Handling Equipment in the Marketplace
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Unlocking the Potential of Container Lifting Equipment
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Essential Equipment in Container Handling: A Comprehensive Overview
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Efficient Solutions for Shipping Container Manipulation
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Efficient Solutions for Container Handling: Equipment Insights
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Efficient Solutions for Container Handling: A Comprehensive Overview
NewsAug.27,2025 -
Welding Fume Composition Analysis
NewsAug.26,2025