- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
Januari . 31, 2025 03:26
Back To List
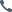
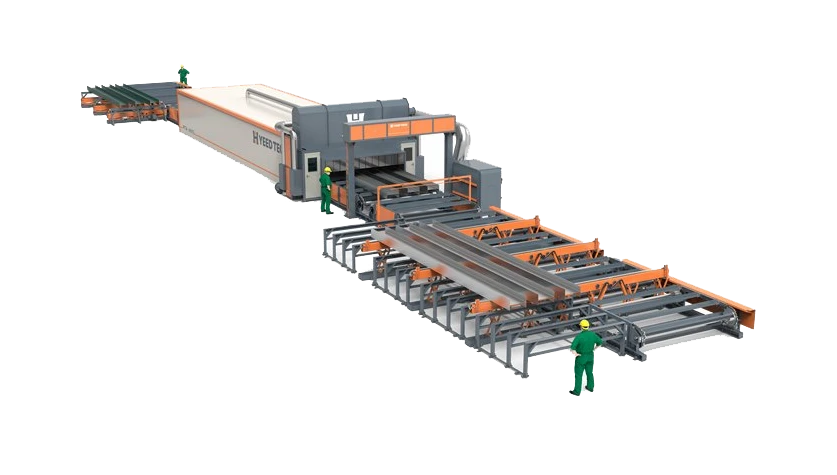
automatic paint dispenser
The landscape of construction is evolving rapidly, with innovation at its forefront. Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) stand as a testament to this evolution, offering unprecedented advantages in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Those familiar with construction trends will find PEBs a fascinating subject for discussion, primarily because of their transformative impact on how modern structures are conceived and erected.
The trustworthiness of pre-engineered buildings is not merely theoretical; it is demonstrated through rigorous testing and real-world application. Manufacturers conduct thorough quality checks on materials and components, ensuring they meet and often exceed industry standards. Additionally, PEBs offer enhanced sustainability credentials, as the precision manufacturing process reduces excess and waste, leading to a lower carbon footprint. This sustainable aspect is particularly relevant to businesses committed to environmentally responsible practices, thereby reinforcing trust through alignment with global sustainability goals. Investments in PEBs are not just about immediate cost reductions but also about long-term financial predictability and operational efficiency. The predictability stems from the reduced variability in project timelines and expenditures—factors frequently cited by project managers as critical to budget planning and resource allocation. The operational efficiency of PEBs is evident in their maintenance, which is often less intensive and costly over the building's lifespan compared to traditional constructions. Innovations in material science continue to enhance the attributes of pre-engineered buildings. Advances in steel alloys and composite materials have expanded the possibilities for PEB applications, accommodating increasingly complex architectural designs. This adaptability ensures that PEBs remain at the forefront of addressing modern construction challenges, from urban expansion constraints to retrofitting requirements in older structures. Ultimately, the adoption of pre-engineered buildings reflects a progressive shift towards smarter, safer, and more responsible construction practices. They represent a fusion of tradition with technology, bringing together the reliability of tried-and-tested methods with cutting-edge innovations. As stakeholders in the construction domain—including architects, engineers, developers, and policymakers—embrace this change, they are likely to further the narrative of PEBs as foundational to the future of building. The growth and continued research into pre-engineered buildings promise an exciting trajectory for those involved in their development and application, underscoring the pivotal role they will play in redefining spaces across the globe.


The trustworthiness of pre-engineered buildings is not merely theoretical; it is demonstrated through rigorous testing and real-world application. Manufacturers conduct thorough quality checks on materials and components, ensuring they meet and often exceed industry standards. Additionally, PEBs offer enhanced sustainability credentials, as the precision manufacturing process reduces excess and waste, leading to a lower carbon footprint. This sustainable aspect is particularly relevant to businesses committed to environmentally responsible practices, thereby reinforcing trust through alignment with global sustainability goals. Investments in PEBs are not just about immediate cost reductions but also about long-term financial predictability and operational efficiency. The predictability stems from the reduced variability in project timelines and expenditures—factors frequently cited by project managers as critical to budget planning and resource allocation. The operational efficiency of PEBs is evident in their maintenance, which is often less intensive and costly over the building's lifespan compared to traditional constructions. Innovations in material science continue to enhance the attributes of pre-engineered buildings. Advances in steel alloys and composite materials have expanded the possibilities for PEB applications, accommodating increasingly complex architectural designs. This adaptability ensures that PEBs remain at the forefront of addressing modern construction challenges, from urban expansion constraints to retrofitting requirements in older structures. Ultimately, the adoption of pre-engineered buildings reflects a progressive shift towards smarter, safer, and more responsible construction practices. They represent a fusion of tradition with technology, bringing together the reliability of tried-and-tested methods with cutting-edge innovations. As stakeholders in the construction domain—including architects, engineers, developers, and policymakers—embrace this change, they are likely to further the narrative of PEBs as foundational to the future of building. The growth and continued research into pre-engineered buildings promise an exciting trajectory for those involved in their development and application, underscoring the pivotal role they will play in redefining spaces across the globe.
Prev:
Products Categories
Latest News
-
Unmatched Mobility and Efficiency in Container Handling Equipment
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Streamlined Approaches and Equipment for Container Handling
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Revolutionizing Cargo Management: Solutions for ISO Container Handling
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Equipment Insights: Revolutionizing Container Handling Operations
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Critical Components for Efficient Shipping Container Handling
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Advanced Equipment and Systems for Efficient Container Storage and Handling
NewsJun.26,2025 -
Unrivaled Components in Structural Engineering Solutions
NewsMay.28,2025