- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
កុម្ភៈ . 05, 2025 01:29
Back To List
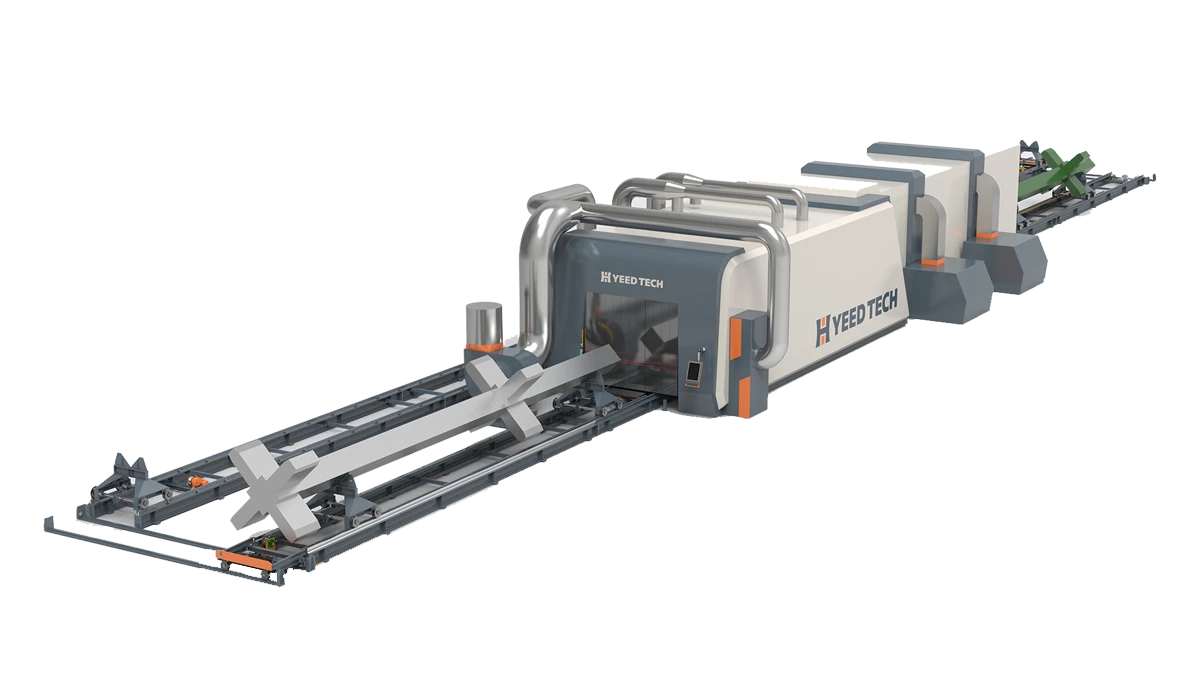
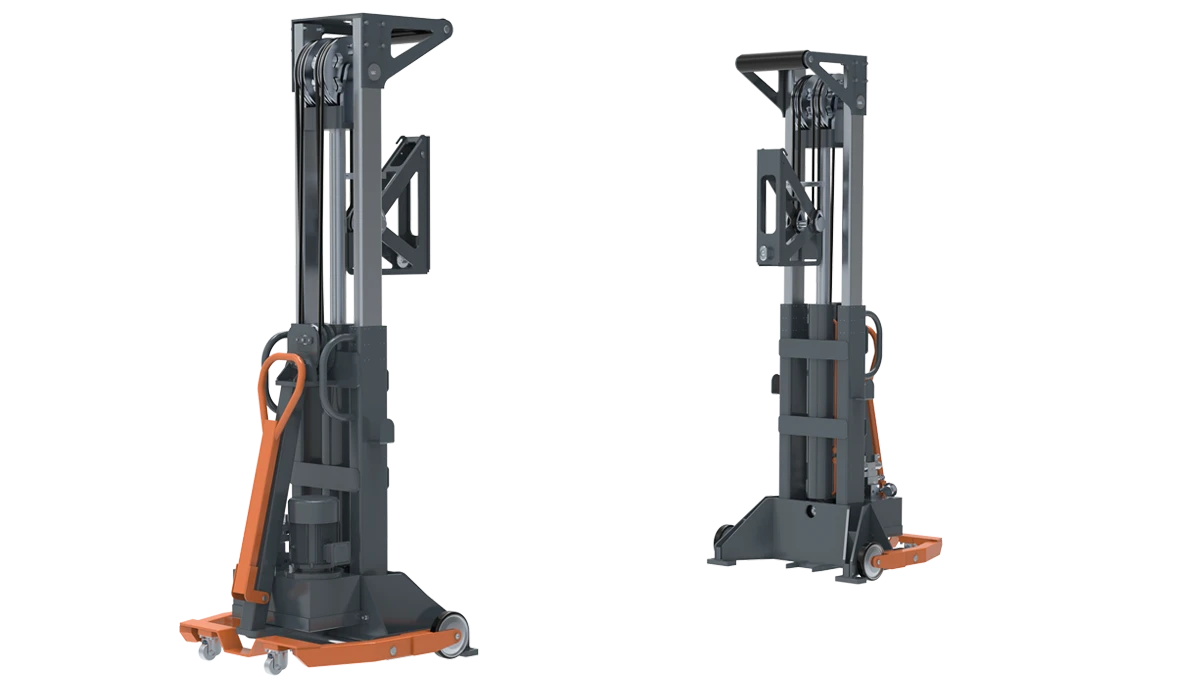
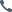
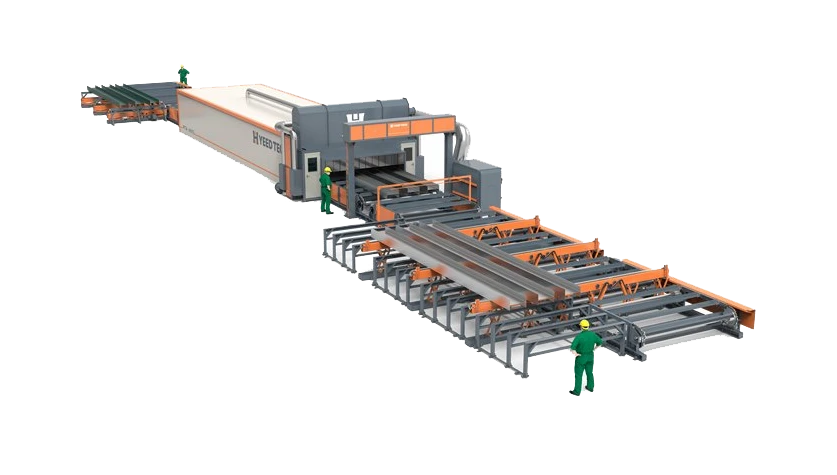
cold formed steel construction
Cold formed steel construction is rapidly transforming the landscape of modern building, offering innovative solutions that cater to contemporary engineering challenges. This method, which involves the shaping of steel sheets at room temperature, bypasses the energy-intensive process of traditional hot rolling, resulting in a material that is both versatile and sustainable.
In terms of real-world experience, case studies serve as compelling testaments to the efficacy of CFS construction. One notable example is the use of cold formed steel in modular housing projects. In these settings, CFS components are pre-fabricated, reducing construction time and enabling rapid deployment of housing solutions. Developers have noted significant cost savings due to reduced labor requirements and accelerated timelines. Moreover, the installment of CFS as part of an offsite construction strategy exemplifies its capability for project scalability and quality control. Pre-fabrication in a controlled environment ensures precision and consistency, while on-site assembly minimizes disruptions and resource waste. These aspects contribute to the ongoing trustworthiness of CFS as a reliable construction method. The role of trust cannot be understated, especially in an industry where safety and durability are paramount. Cold formed steel's track record in withstanding seismic events, high winds, and other environmental stressors plays a crucial role in building confidence among stakeholders. Structures built with CFS have been found to meet or exceed seismic performance expectations, a testament to their resilience in the face of natural disasters. In conclusion, cold formed steel construction is a robust, reliable, and revolutionary approach that meets the demands of modern building with unmatched efficiency. Its compelling blend of strength, flexibility, sustainability, and safety continues to gain favor across the construction industry. By adhering to established guidelines and continually engaging with innovations in material science, professionals can harness the full potential of CFS to deliver exceptional structures that stand the test of time.
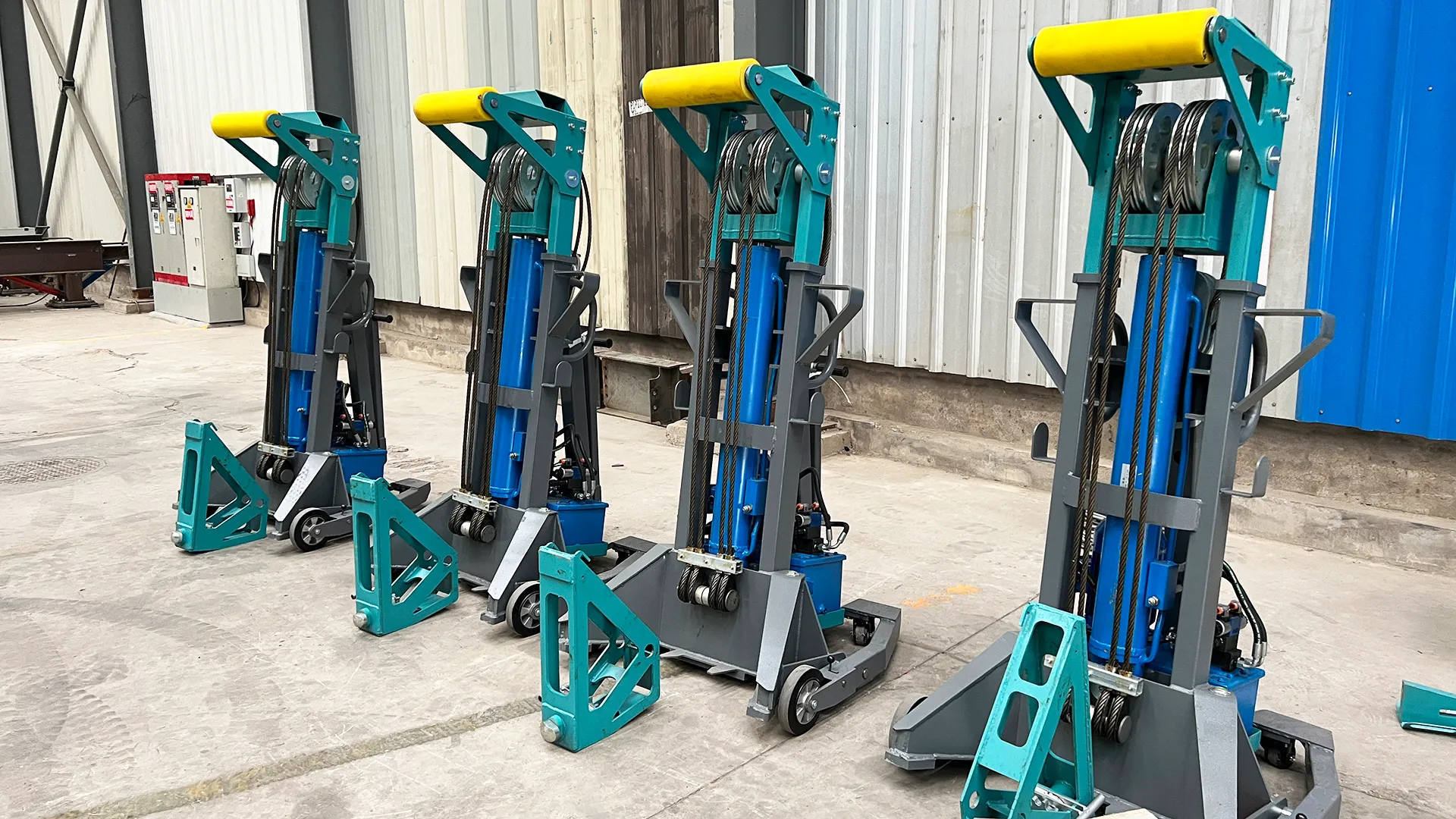


In terms of real-world experience, case studies serve as compelling testaments to the efficacy of CFS construction. One notable example is the use of cold formed steel in modular housing projects. In these settings, CFS components are pre-fabricated, reducing construction time and enabling rapid deployment of housing solutions. Developers have noted significant cost savings due to reduced labor requirements and accelerated timelines. Moreover, the installment of CFS as part of an offsite construction strategy exemplifies its capability for project scalability and quality control. Pre-fabrication in a controlled environment ensures precision and consistency, while on-site assembly minimizes disruptions and resource waste. These aspects contribute to the ongoing trustworthiness of CFS as a reliable construction method. The role of trust cannot be understated, especially in an industry where safety and durability are paramount. Cold formed steel's track record in withstanding seismic events, high winds, and other environmental stressors plays a crucial role in building confidence among stakeholders. Structures built with CFS have been found to meet or exceed seismic performance expectations, a testament to their resilience in the face of natural disasters. In conclusion, cold formed steel construction is a robust, reliable, and revolutionary approach that meets the demands of modern building with unmatched efficiency. Its compelling blend of strength, flexibility, sustainability, and safety continues to gain favor across the construction industry. By adhering to established guidelines and continually engaging with innovations in material science, professionals can harness the full potential of CFS to deliver exceptional structures that stand the test of time.
Next:
Products Categories
Latest News
-
Unrivaled Components in Structural Engineering Solutions
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Transforming Spaces with Diverse Steel Structures
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Steel Structural Elements: A Comprehensive Overview of Construction Solutions
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Optimizing Steel Structures: Paint Solutions, Assembly, and Design
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Fortifying Steel Structures with Intumescent Coatings and Design Excellence
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Enhancing Structural Integrity and Aesthetics with Specialized Construction Materials
NewsMay.28,2025 -
Unlock the Power of Modern Steel Structure Manufacturing with Advanced Equipment
NewsMay.27,2025